
+1 888 123 4567
Zoom Share Audio: A Comprehensive Guide
If you're looking to enhance your Zoom meetings by sharing computer audio effectively, you're in the right place. Zoom has two primary methods for sharing computer audio, and we'll walk you through both of them.
Sharing Computer Audio Through Screen Sharing
Imagine you're in a traditional classroom, and everyone can hear the audio from a shared source. Zoom share audio option allows you to achieve the same effect in a virtual setting.
Methods: There are two ways to share computer audio on Zoom:
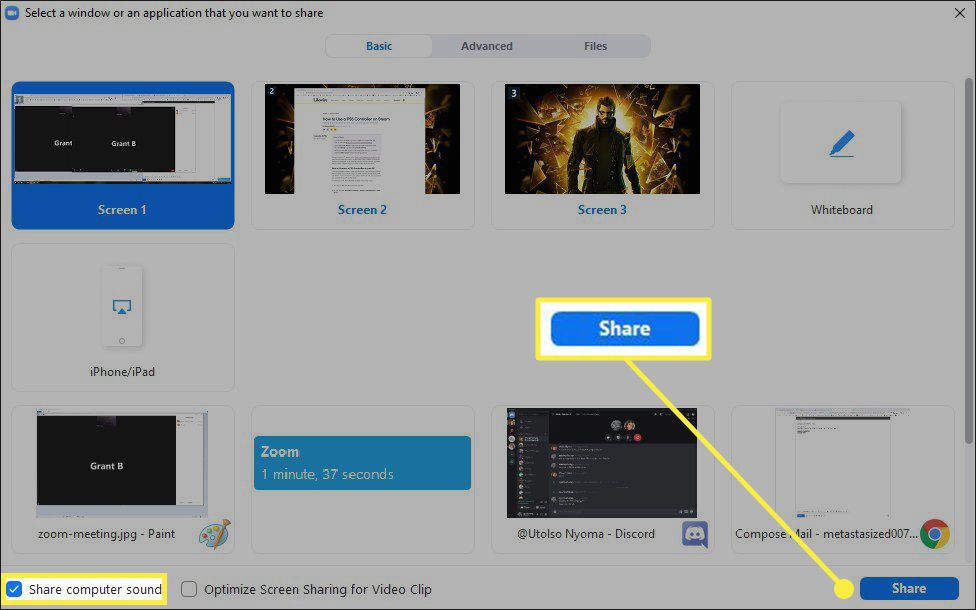
a. Screen Sharing: Share your screen and play the audio directly from your computer. This ensures everyone hears it clearly.
b. Advanced Settings: Under 'Advanced,' you can choose to share computer sound only, without sharing your screen.
Steps:
When you share your screen, make sure to tick the 'Share computer sound' option.
This feature allows you to share videos and audio seamlessly with your students or audience.
Video and Lighting: Good lighting and audio quality are essential for effective Zoom sessions. Consider recommended lighting setups and microphone options for better results.
Practical Demo: The article author mentions using QuickTime to record the Zoom session, demonstrating the audio quality when recording a video.
Wrap-Up: These methods offer flexibility for sharing audio in your Zoom meetings, whether you're teaching or presenting. Remember to explore different applications, such as teaching English listening skills.
Alternative Audio Sharing
If you're not sharing visuals, you can use Zoom's 'Advanced' settings to share audio directly without video.
Conclusion
Incorporating these methods into your Zoom meetings can greatly improve the quality of audio sharing, enhancing the learning experience for your audience. Feel free to explore other articles on Zoom usage and equipment recommendations for more insights.
RDS vs RDP: A Comprehensive Guide to Remote Desktop Services
In the digital age, remote access to computers and servers has become a critical component of many businesses and organizations. Two commonly used terms in this context are RDS (Remote Desktop Services) and RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol). Understanding the differences between these two is essential for efficient remote access management. In this article, we will explore RDS vs. RDP, their functionalities, and when to use each.
What is RDS (Remote Desktop Services)?
Remote Desktop Services is a comprehensive suite of tools and services offered by Microsoft. It allows organizations to create a virtualized desktop infrastructure (VDI) and deliver applications and desktops to users over a network. RDS provides several key features: Let’s know about the features and find out the winner of the battle of rds vs rdp.
Application Virtualization: RDS allows you to host and manage applications centrally, making them accessible to remote users.
Desktop Virtualization: It enables the creation of virtual desktops, allowing users to access a full desktop environment remotely.
Session Virtualization: RDS offers session-based remote desktops, where multiple users can share a single server.
Load Balancing: RDS includes load balancing features to distribute user sessions across multiple servers for better performance.
What is RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol)?
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), on the other hand, is a protocol developed by Microsoft that facilitates remote access to computers or servers. It is the underlying technology that powers remote desktop applications like Microsoft Remote Desktop. Key aspects of RDP include:
Remote Control: RDP enables users to take control of a remote computer or server's desktop as if they were physically present.
Secure Connection: It uses encryption and authentication to ensure secure data transmission between the local and remote devices.
Platform Independence: RDP clients are available for various platforms, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and mobile devices.
File and Resource Sharing: RDP allows users to share files and resources between the local and remote systems.
When to Use RDS or RDP?
The choice between RDS and RDP depends on your specific needs:
RDS: Use Remote Desktop Services when you need to provide multiple users with access to a shared desktop or application environment. It's suitable for businesses that require centralized control and management of virtualized resources.
RDP: RDP is ideal when you want to access a single remote computer or server directly. It's commonly used for IT administration, troubleshooting, or accessing personal computers remotely.
Conclusion
RDS and RDP serve distinct purposes in the realm of remote access. Remote Desktop Services offers a comprehensive solution for organizations looking to manage and deliver desktops and applications to multiple users. In contrast, Remote Desktop Protocol provides the means for remote control of individual computers or servers. Understanding these differences will help you make informed decisions regarding your remote access strategy.